WAVE Team 6 Nuertingen 2021: Difference between revisions
| Line 126: | Line 126: | ||
*''map the land uses along your water areas: settlements, infrastructure, agriculture, resource extraction, natural areas, energy production...'' | *''map the land uses along your water areas: settlements, infrastructure, agriculture, resource extraction, natural areas, energy production...'' | ||
*''describe in particular the historical evolution of land use pattern, please make use of historical maps'' | *''describe in particular the historical evolution of land use pattern, please make use of historical maps'' | ||
Historically, Along the Neckar River, Nürtingen have been established on the top of a hill, preventing the populations from flood events. The landscape was transformed by local people involved into diverse kind of agriculture and wood logging. | |||
However, from 1824 to 2021 in Nürtingen, we can observe a large transformation of the landscape and a very strong growth of the settlements. Some urban has sprawl down to the floodplain’s areas, and the agriculture field have become less diversified, wider and closer to the river. | |||
'' | |||
*''description evolution, status quo and driving forces, is the land use likely to change? Why is that? (approx 200 signs)'' | *''description evolution, status quo and driving forces, is the land use likely to change? Why is that? (approx 200 signs)'' | ||
The strong economy of the Stuttgart region is a major driver of change in the urbanisation of the Neckar River. The industries have grown very quickly and create a rising demand for transport on the river, electricity plants, construction of road and highway along the river. | |||
Furthermore, Industrialization of agriculture have transformed largely the natural landscape of the region. | |||
The Stuttgart region significant and steady growth of its population and the scarcity of homes available is creating opportunities in real estate market to develop more space for living. And the Covid pandemic increase the demand of the population to relocate themself away from major urban centers. | |||
The land occupation will change according to economic success of the Stuttgart region and technologies such as electricity production will have an impact on the river ecology. Agriculture will also change eventually to a more nature base approach and allow biodiversity to occupy the territory. More and more people will work from home into services industries and the urban sprawling will continue to growth and will have an impact on the landscape. Hopefully, people will get in touch more with the river and the land so it can create new driver of change toward bio-diversified landscape. | |||
'' | |||
*''add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like'' | *''add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like'' | ||
Revision as of 05:42, 26 April 2021
>>>back to working groups overview
| Area | Baden-Württemberg | |
| Place | Nürtingen | |
| Country | Germany | |
| Topics | WAVE Project | |
| Author(s) | Gabriel, Yana, Digjam, Titiksha, Manasviben | |

| ||
Rationale
- Why do you think this case is relevant? What is your hypothesis considering the landscape challenges?
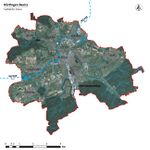
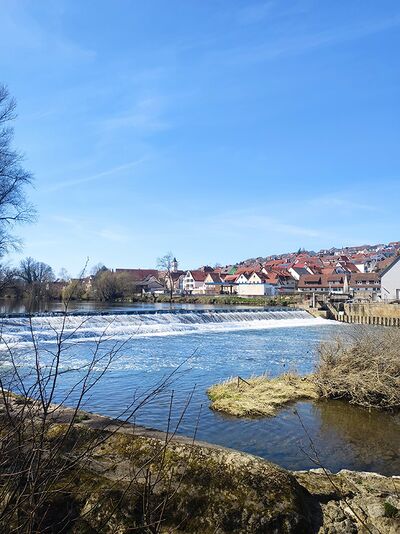
The main parts of the city of Nuertingen extend along the fast-flowing river Neckar, such as the center of this city, Neckarhousen, Oberensingen, and Zizishausen. Proximity to the freshwater is an important factor for the life of the citizens and for the animals. However, lack of accessibility, regular air, and water pollution have an effect on the sustainable future of this city, as well as flood events, which are the biggest challenges of the Neckar River.
Location and scope
You can edit this map with the map editor
Water as a natural system
Geomorphology, typologies and dynamics of water areas
- Describe the water areas of your area in the context of the wider water system
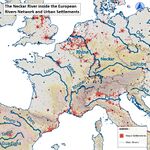
Neckar is a major tributary of the Rhine River at Mannheim. Rising at the Black forest and flow through a steep valley in the Odenwald Mountain and also passes through Tubingen, Nurtingen, Esslingen, Stuttgart, and Heidelberg.
Neckar valley water system can be classified between three segments:
In the Northern, from Kirchheim to Stuttgart, the upper course closest to the source of River Rhine. Narrow and steep gradient with vineyards and highly affected by vertical erosion and striking rock formation but only has 6-meter height waterfall at DeisslingenLauffen, where rapids were occasionally seen at Lauffen at Neckar when erosion occurs and gorge found in the Odenwald the district of Neckargerach at Neckar.
In the Central, from Stuttgart to Plochingen, the middle course is characterized by Urban structure, cultural and landscape diversity where a river starts to slow down, get wider, and travels in a winding loop having a lot of lateral erosion, transportation, and deposition. Floodplains meander, oxbow was founded in the history of River Neckar. Neckar’s oxbow was established when the Neckar loops were penetrated in the year 1933-1934 where expansion and canal were created.
In the Southern, from Plochingen to Neckartenzlingen, the lower course is the final segment where the river gradient is at its gentlest, as the river approaches the sea, it has a wider smooth channel and moves at its slowest speed where large flood plains, deltas, and estuaries levees found. Here ship no longer can pass through, Orchards and lands of wood were also found with some residential and industrial areas
- How does water appear in the landscape of your living lab? What types of water areas are common?
The Neckar is 362 kilometers longer (225 mi), the Neckar valley is cut in the deepest by over 400 meters through the mountains Water appears in many forms depending on the natural geomorphology, typologies, and dynamics of its flow. In a wider context watershed, drainage basin, catchment area or the cultural or built environment by humans is also responsible for its appearance, the River, Lakes, Ocean, Sea, Tributaries, Streams, Puddle, Pond, Canals and Floodplains are the types of water areas that are common in our Living Labs
- Please identify the water bodies' catchment areas, tributaries, and floodplains
Catchment: The River Neckar catchment area is 13,900 km2 (5,378 sq mi) is located in the southwest part of Germany and is a tributary of the River Rhine valley. Tributaries Eschach, Prim, Schlichem, Glatt, Eyach, Starzel, Steinlach, Ammer, Echaz, Erms, Aich, Lauter, Fils, Korsch, Rems, Murr, Enz, Zaber, Schozach, Lein, Sulm, Kocher, Jagst, Elz, Ltter, Laxbach, Steinach, Elsenz. Floodplains: Tributaries of river Neckar, Danube, Rhine, the Seine at the German state of Bavaria, Hessen, Rhine-Palatinate, Baden-Wurttemberg and North Rhine-Westphalia were affected floodplains
- Which dynamics do these water areas have?
The Dynamic equilibrium of the River Neckar subjected to the topography of the middle-Neckar River region is surrounded by two mountains, the western black forest, and the south-east Swabian Alb, the river valley of Neckar at someplace in region, carved in the gently rolling hilly land and opens up into the vast plains. The Neckar sized 14000 km2, covering 40% of the total area of Baden-Württemberg, An area where about half of the population of the state live, which is situated primarily on the lee-side of the Vosges mountain. Overlapping the 200 year ago map we can observe that the river flow has been artificially channelized and sifted from its original position due to urbanization and human Intervention. The water flow is faster because channels are provided long and straightforward.
- Have there been any flood events in the past?
Yes, there have been many events in the past, the extreme flood events in central Europe were in the last two decades. • The flood events along the River Elbe in 2002. • The Flood after several days of heavy rainfall in June 2016. • Several flood events happened in 1993 on Neckar catchment.
- add 2-3 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
Water as a living space
- Which habitats can be found in and along the water areas of your area?
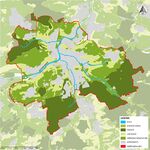
Formation of habitats on the territory of the city Nurtungen has resulted to a combination of factors such as history, climate, geographical location, flora, and fauna of surrounding territories. The morphology of the territory also has a strong impact on the way of forming habitats. The city lies on the river Neckar, a mountain fast-flowing river, as well as a hydrographic network is represented by streams and small freshwater lakes. Leading development the city of Nuertingen, recapturing large areas of land, due to this, complex areas with alternating natural vegetation, farmlands, and urban territories are formed. Classification of habitats that can be found along and in the water of the river Neckar: Wetlands – marshy area, banks of the river, floodplain; Freshwater – riverine, streams, lakes; Urban – recreation, residential areas, gardening, and landscape design; Forest – old and young forests; Farmlands – pasture and orchards; Grassland – meadows, and slopes;
- How is the water quality in your water areas?
The Neckar in the territory of the Nurtingen runs through 3 dikes that slow down the river’s flow. In some locations can be found the dense settlement, especially along streams, and sewage treatment plants. As a result, a high nutrient proportion can be recorded, which leads to the significant development of algae during the summertime. The lack of oxygen due to the degradation of this organic material can be dangerous for many wetland and freshwater species. The warning level of continuously recorded oxygen by the power station is below 4 mg per liters. The level of pH of river water is also a very important parameter – the measure of hydrogen ion concentration. Low pH can be dangerous to immature fish and insects, while the high level of pH is also harmful to most organisms. The most optimal pH level which is considered for life – 7,4. The level with indicator 8.0 can be sufficient for most river species, but clams and snails usually prefer the higher level of pH. According to the last measurements the pH value in the river Neckar in the territory of the Nuertingen – 8,3.
- Which areas are still natural, which are urbanised/artificial?
The structure of the river and streams bodies is a very significant parameter, which contains bed and bank structures, course development, transverse and longitudinal profiles and watercourse environment. This parameter must be recorded because of two important reasons: - habitats should be available for well-being in and around the river; - flora should be naturally occurring in and along the river and streams; Baden-Württemberg water structure map shows that structure which was considerably changed and significantly changed with the largest share of the total assessments. There are about 40% of the river structure in an unchanged, slightly changed, and moderately changed condition. The results of structural completely changed class are composed of the waters that as a result of the individual parameters piped sections, this corresponds to approximately 20% of the total rated.
- Are the rivers permeable for fish or blocked by artificial elements?(approx 200 signs)
Since the Neckar river in the territory of the Nurtingen flows through 3 dikes it can block migration of fishes because these dikes have electro station and turbines, that dangerous for fishes’ lives. However, when analyzing and observing the river Neckar some artificial structures were sighted, next to the dikes, which provide an opportunity for free movement of fishes. These structures represented a new way for the fish migration separate from river flow towards to turbine. All calculations were done by specialists, according to the speeds of the river’s flow and observing the fish migration. These lots for the movement have stepped construction that allows fishes to have a rest after the long migration. In conclusion, the river Neckar has serious artificial elements that can block the movement of fishes, but some good solutions can be found along the river, so this part of the river is permeable for fish at this moment.
- add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
Blue and Green Infrastructure
- What are the major potential elements of a green/blue infrastructure network? Are these likely to change/disappear? Why is that?
- You find my background material on green infrastructure in our reading list
- add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
Water as a cultural space
Land use and water
- map the land uses along your water areas: settlements, infrastructure, agriculture, resource extraction, natural areas, energy production...
- describe in particular the historical evolution of land use pattern, please make use of historical maps
Historically, Along the Neckar River, Nürtingen have been established on the top of a hill, preventing the populations from flood events. The landscape was transformed by local people involved into diverse kind of agriculture and wood logging.
However, from 1824 to 2021 in Nürtingen, we can observe a large transformation of the landscape and a very strong growth of the settlements. Some urban has sprawl down to the floodplain’s areas, and the agriculture field have become less diversified, wider and closer to the river.
- description evolution, status quo and driving forces, is the land use likely to change? Why is that? (approx 200 signs)
The strong economy of the Stuttgart region is a major driver of change in the urbanisation of the Neckar River. The industries have grown very quickly and create a rising demand for transport on the river, electricity plants, construction of road and highway along the river.
Furthermore, Industrialization of agriculture have transformed largely the natural landscape of the region.
The Stuttgart region significant and steady growth of its population and the scarcity of homes available is creating opportunities in real estate market to develop more space for living. And the Covid pandemic increase the demand of the population to relocate themself away from major urban centers.
The land occupation will change according to economic success of the Stuttgart region and technologies such as electricity production will have an impact on the river ecology. Agriculture will also change eventually to a more nature base approach and allow biodiversity to occupy the territory. More and more people will work from home into services industries and the urban sprawling will continue to growth and will have an impact on the landscape. Hopefully, people will get in touch more with the river and the land so it can create new driver of change toward bio-diversified landscape.
- add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
Cultural and spatial typologies of water areas
- Which spatial patterns have evolved in relation to your water areas?
- What is the role of water areas within the overall urban morphology? (approx 200 signs)
- add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
- Yourcase water space1.jpg
add a caption
- Yourcase water space2.jpg
add a caption
- Yourcase water space3.jpg
add a caption
Sacred spaces and heritage
- Which places/elements hold cultural value and to whom?
- You may add a map and some images, please also explain in your caption why these elements are valuable
- Your case sacredspace1.jpg
add a caption
- Your case sacredspace2.jpg
add a caption
- Your case sacredspace3.jpg
add a caption
Visual appearance and landscape narrative
- Which elements are essential for the landscape character?
- Has the landscape been painted or otherwise depicted, when and whom? Which elements are essential?
- Which narratives exist? Who has written about this landscape or depicted it in some way?
- You can add text and images
- Your case character1.jpg
add a caption
- Your case character2.jpg
add a caption
- Your case character3.jpg
add a caption
Water and People
Accessibility and usability
- Where are your water areas accessible, and where not? How strong are spatial obstacles preventing access?
According to survey analysis, only a small part of the river Neckar in the territory of the city Nuertingen is accessible for people – a cycling and walking path from the center to the sports area on the southern part of the river and a small area on the northern part of the riverbank between two pedestrian bridges. Other parts have serious problems with access to the river, especially Neckarhausen, which is separated from the river by the main and noisy Neckarstrasse road. Also, the residential area along the Muhlstrasse has constructions and “jungle” river banks that prevent people from visiting river Neckar.
- Who is using the spaces and how?
Citizens of Nuertingen enjoy walking along the river, such as older people and young families with children, people who love to do sports activities, such as cyclists and joggers can be found in the territory of riverbanks. Also, fishermen choose the south side of the river for fishing because this area has the quiet atmosphere for animals.
- Yourcase youraccessbilitymap.jpg
add a caption
Community Mapping
What is to be mapped here?
- Social groups from within the community, for example the youth, kids, students, parents, the retired etc. Typically, these groups have specific needs, which you can also make explicit on the map. These people might not be organized in any way, but they are usually present in the context you are observing
- Local stakeholder groups: these groups are organized in one or the other way. They only exist within the community context you are observing. For example: the local community center, local churches, local interest groups, the landowners, small businesses and retailers
- External stakeholder groups are not necessarily present in the environment you are observing, but they may have strong stakes and interests. These can be local authorities, politicians, associations, care services etc.
- For each group, you may identify their needs, objectives, power and capacities
- You may also identify gaps and power conflicts
- Please try to redepict these elements in an integrated way and in relation to your water landscape. What is the relationship between these groups? Are they close or distanced from each other? Who is more powerful? Which voices are hardly heard? Do they have any shared concerns?
- Your case your community map3.jpg
add a caption
Possible Futures
- You can summarize your findings with a SWOT diagram and a DPSI(R) Model
- Link back to the Sustainable Development Goals: Which goals are at risk?
- What is your worst case scenario for this landscape?
- What is your best case scenario for this landscape?
- Present your scenarios in the form of a collage or sketch
- Add text and visuals
- Your case your spider diagram or dpsir model.jpg
explain your analysis briefly in the caption
- Your case yourworstcase visual.jpg
explain your worst case scenario briefly in the caption
- Your case yourbestcase visual.jpg
explain your best case scenario briefly in the caption
Collaborative Goal Setting
- Define strategic planning objectives based on the evaluation findings from your analysis
- Ideally, involve the community of your living labs into this process
- Link back to your original targets from section one and the Development Goals
- 150 words text contribution
Spatial Strategy and Transect
- translate your strategic goals into a vision
- develop a spatial translation of your vision
- exemplify your vision in the form of a transect with concrete interventions
- add map(s) and visualizations
- Your case spatial translaton vision.jpg
add caption here
- Your case transect.jpg
add caption here
- Your case transect detail1.jpg
add caption here
- Your case transect detail2.jpg
add caption here
From Theory of Change to Implementation
- For implementing your vision: Which partnerships are needed? Which governance model is required?
- Who needs to act and how? Draw and explain a change/process model/timeline
- Which resources are needed? On which assets can you build?
- add 150 words text and visuals
References
- give a full list of the references you have used for your case
Process Reflection
- Reflect in your intercultural and interdisciplinary team on the outcomes of your study
- Which limitations were you facing?
- What have you learnt from each other?
- What did you learn in the Living Labs?
- What would you do differently next time?
- You can also use diagrams/visuals
- 250 words text