WAVE Team 4 Nuertingen 2021
>>>back to working groups overview
| Area | Baden-Württemberg | |
| Place | Nürtingen | |
| Country | Germany | |
| Topics | WAVE project | |
| Author(s) | Arash, Ekbal, Mohadese, Samira, Yuga | |

| ||
Rationale
- Why do you think this case is relevant? What is your hypothesis considering the landscape challenges?
Overcoming the flooding is One of the biggest challenges of the Neckar River, especially one of its tributaries, Tiefenbach. Due to urban development and other factors, many parts of the river have changed and are out of their original form. This region has many cultural and social potentials that can be developed in the desired direction by planning.
Location and scope
You can edit this map with the map editor
Water as a natural system
Geomorphology, typologies and dynamics of water areas
- Describe the water areas of your area in the contxt of the wider water system
The River Neckar in Germany starts from the Black Forest the southwest of Baden-Württemberg at a height of 706m above sea level and it continues 362 kilometers long and it passes through Nürtingen city and reaches river Rhine at a height of 95m above the sea level.
- How does water appear in the landscape of your living lab? What types of water areas are common?
Neckar River is one of the most significate river in Nurtingen living lab. The river Neckar flows north and northeast, along the northwestern edge of the Swabian Alb passing Nürtingen and other small cities and melt into the river Rhine. There are some small river namely Tiefenbnach Steinach, Aich, Marbach, Aischenbach formed from Neckar river in the Nurtingen area. There are three types of water area are common on this living lab. - Rivers water - Tributaries water - Lakes water (Standing Water)
- Please identify the water bodies' catchment areas, tributaries and floodplains
The main sources of water in the living lab are rivers and their tributaries among them river Neckar is the most significant. Furthermore also some Lakes are contributes water they are oberer fischersee, unterer fischersee, Beutwangsee and tiefen-loch-see.
Basic catchment area of Nürtingen living lab river basin. Tiefenbnach and Rietbach river basin have 1,981 km2 catchment area. Neckar, steinach and tiefenbach river basin have 157 km2 catchment area. Neckar, seebach and steinach river basin have 473 km2 catchment area. Steinach and Humpfenbach river basin have 1,522 km2 catchment area. Steinach, Plaice tobel and Humpfenbach river basin have 999 km2 catchment area. Neckar, Tiefenbach and Aich river basin have 777 km2 catchment area.
Flooding is the most significant challenge/issue for the Nürtingen living lab. Municipality identifies some specific floodplains area and implements a plan for flood protection zone surrounding Neckar River. Also, there are some flood protection dams that partially save Nürtingen city from floods.
- Which dynamics do these water areas have?
- Have there been any flood events in the past?
There have been 4 floods in Neckar History: In 1926 The Saubach overflowed its banks, in 1978 Flood in Oberensingen and on the B313, in 1990 Flood in Neckarhausen, in 2013 Neckar flood, city center Nürtingen.
- add 2-3 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
- Yourcase watersystem2.jpg
add a caption
- Yourcase watersystem3.jpg
add a caption
Water as a living space
- Which habitats can be found in and along the water areas of your area?
- How is the water quality in your water areas?
Unfortunately Water quality in this region is declining annually, based on samples taken in parts of the river, the average pH of water in 1995 was 8.2, in 2000 8.2, and in 2018 about 8.4. This indicates that factors have caused the water of this river to become acidic.
- Which areas are still natural, which are urbanised/artificial?
Around the city centre, the river structures are "completely changed", the river goes under ground, and "very much changed" so to speak artificial river. However, along the land use of agricultural and forest is quite natural.
- Are the rivers permeable for fish or blocked by artificial elements?(approx 200 signs)
- add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
- Yourcase wateraslivingspace3.jpg
add a caption
Blue and Green Infrastructure
- What are the major potential elements of a green/blue infrastructure network? Are these likely to change/disappear? Why is that?
In 2018 and 2019, the city of Nürtingen and BUND, together with other actors, will implement several biotope network measures. These serve as models for other municipalities and cities and have a pioneering role within Nürtingen for future biotope network measures. Renovate dry stone walls: Dry stone walls are not only useful for sand lizards and wild bees, which love sunny spots, as a habitat. Rather, they protect the ground from slipping on slopes and make up the unmistakable character of our cultural landscape. On the Grubberg in Nürtingen-Oberensingen, many dry stone walls have fallen into disrepair and are overgrown with nettles and grasses. As a result, they are shaded, damp, and no longer fulfill the functions mentioned above. In cooperation with the nature conservation associations BUND and NABU, the city of Nürtingen is promoting the renovation of the walls. Promote biodiversity in the field: The northwest of Nürtingen is known as an intensive arable area with special crops such as strawberries and asparagus. The aim here is to develop stepping stones rich in flowers and wild plants, which enable a higher number of species and individuals of insects such as butterflies and grasshoppers. Together with the plant seeds, these can serve as food for endangered fields bird species such as the skylark, the gray bunting, or the partridge. Farmers who want to give a piece back to nature provide their own areas for this purpose. Good to know: If you own or cultivate grassland or arable land, you can receive financial compensation under certain conditions, for example, if you leave fields and roadsides unsprayed or develop fallow land. Talk to us if you are interested in the natural design of your space! The Neckar bike path in Nürtingen and the surrounding area: One of the most important and valuable elements of Green Infrastructure in this region is The Neckar bike path in Nürtingen. This beautiful cycling route is about 370 km long and is one of the best and most attractive cycling routes in Germany. The main purpose of this route is to create a beautiful view along the river. Locals use this route to access different parts of the city. This Path connects the blue and green infrastructure near Neckar River.
- You find my background material on green infrastructure in our reading list
- add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
Water as a cultural space
Land use and water
- map the land uses along your water areas: settlements, infrastructure, agriculture, resource extraction, natural areas, energy production...
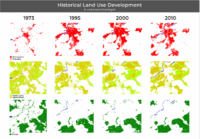
- describe in particular the historical evolution of land use pattern, please make use of historical maps
The city of Nürtingen has undergone many changes in settlement areas over the past decades. The expansion of the industrial area through the destruction of gardens and farms is very significant. According to Nürtingen historical maps, there were many wine gardens, which over time gave way to various agricultural lands.
- description evolution, status quo and driving forces, is the land use likely to change? Why is that? (approx 200 signs)
According to Natura 2000, many green areas are protected and changes are fully controlled. According to future plans to prevent floods, there is a possibility of changes in the residential and industrial parts of the city.
- add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
Cultural and spatial typologies of water areas
- Which spatial patterns have evolved in relation to your water areas?
- What is the role of water areas within the overall urban morphology? (approx 200 signs)
In the course of the city's development, as depicted in the pictures and photographs, the urban landscape with its farms, churches, and historical buildings around the Neckar River was the core of Nürtingen. From the photographic material that we have been able to collect, we can see that in 1683 Nürtingen played a role in the supply of water and energy for agriculture, and in 1817 the first factory of the Baumwollspinnerei Otto (cotton mill) was established in Nürtingen, which marked the beginning of the development of the industrial city. From 1927 onwards, the city was partly transformed and a power station was built to harness the water power of the Neckar River. From the old maps that could be collected, it can be seen that in the 1980s, the Tiefenbach River, a tributary of the Neckar River, was partly covered by the ground in the city center and the northern part of the city center was developed. In 2013, the Neckar River was revisited as a sustainable waterfront space with the creation of a fish migration bypass and recreational spaces for people such as decks. sustainable waterfront space.
- add 1-2 graphical representations to the image gallery, you can add more if you like
- Yourcase water space2.jpg
add a caption
- Yourcase water space3.jpg
add a caption
Sacred spaces and heritage
- Which places/elements hold cultural value and to whom?
・Since Nürtingen is a very old city (dating back to the 6th and 7th centuries) there are places and elements of historical value in it, especially in the central part of the city, which are of great importance for both citizens and tourists. These historical places also have an important identity role for the city.
・Here are some of these historic sites: ・City Church of Saint Laurentius (Laurentiuskiche): Laurentius is located on a hill by the river Neckar. It is a landmark that dominates the town of Nürtingen. Dedicated to St. Laurentius (St. Lawrence),the original church was probably built in the 10th or11th century. ・Historic old town : The location of the old town centre of Nürtingen on the spur of a hill overlooking the Neckar Valley, with a far-reaching view over the surrounding countryside and a dominant position over the Neckar crossing, indicates that the original site was of strategic importance. ・The town hall ・The Block tower: The Block tower was built in 15 century.
- You may add a map and some images, please also explain in your caption why these elements are valuable
- Your case sacredspace2.jpg
add a caption
- Your case sacredspace3.jpg
add a caption
Visual appearance and landscape narrative
- Which elements are essential for the landscape character?
Landscape character assessment is basically searching for the uniqueness quality of a particular local landscape and its help to build up different types of landscape in different rejoin. The different elements of landscape are including underlying geology, soils, topography, water, air, land cover hydrology, land use settlement, landform vegetation, physical feature, physical and cultural development and how all the features combined together to make one rejoin over all character separate from another.
- Has the landscape been painted or otherwise depicted, when and whom? Which elements are essential?
- Which narratives exist? Who has written about this landscape or depicted it in some way?
- You can add text and images
- Your case character1.jpg
add a caption
- Your case character2.jpg
add a caption
- Your case character3.jpg
add a caption
Water and People
Accessibility and usability
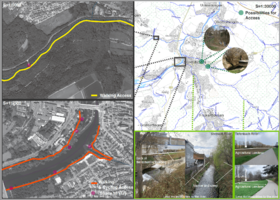
- Where are your water areas accessible, and where not? How strong are spatial obstacles preventing access?
People can access and stay in places like calm and stable areas. Rocks, benches, and other places present comfortably to stay longer. An area with a mixture of inaccessible spaces and comfortable spaces, such as flat areas or slopes where people can sit, contributes to both ecology and people. On the other hand, like steep path and artificial river like a dike, will keep people away.
- Who is using the spaces and how?
On the riverside path, people of diverse ages enjoy cycling, jogging, and walking. On the deck overhanging the river, runners and walkers stop for a short break to admire the scenery and enjoy small conversations. Most young people enjoy talking in the sand area and flat area as a group. Where the water is flowing at such a speed that it becomes a pool for fish, there are people fishing. If the riverside is farmland, there is no space for people to stop and the river is close to its natural state. At the gentle steep very close to the river, the family enjoys playing in the water with dogs. One to two people sit and gaze at the riverscape surrounded by green and calm areas.
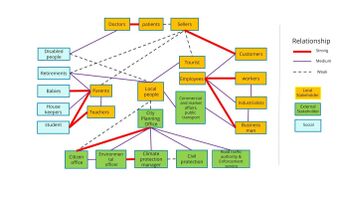
Community Mapping
What is to be mapped here?
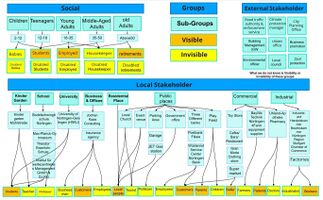
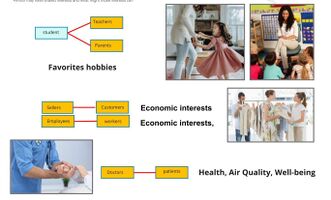
- Social groups from within the community, for example the youth, kids, students, parents, the retired etc. Typically, these groups have specific needs, which you can also make explicit on the map. These people might not be organized in any way, but they are usually present in the context you are observing
- Local stakeholder groups: these groups are organized in one or the other way. They only exist within the community context you are observing. For example: the local community center, local churches, local interest groups, the landowners, small businesses and retailers
- External stakeholder groups are not necessarily present in the environment you are observing, but they may have strong stakes and interests. These can be local authorities, politicians, associations, care services etc.
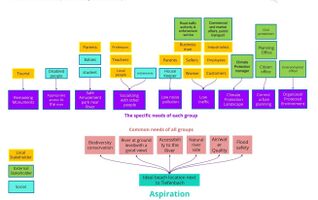
- For each group, you may identify their needs, objectives, power and capacities
- You may also identify gaps and power conflicts
- Please try to redepict these elements in an integrated way and in relation to your water landscape. What is the relationship between these groups? Are they close or distanced from each other? Who is more powerful? Which voices are hardly heard? Do they have any shared concerns?
Possible Futures
- You can summarize your findings with a SWOT diagram and a DPSI(R) Model
- Link back to the Sustainable Development Goals: Which goals are at risk?
- What is your worst case scenario for this landscape?
- What is your best case scenario for this landscape?
- Present your scenarios in the form of a collage or sketch
- Add text and visuals
- Your case your spider diagram or dpsir model.jpg
explain your analysis briefly in the caption
- Your case yourworstcase visual.jpg
explain your worst case scenario briefly in the caption
- Your case yourbestcase visual.jpg
explain your best case scenario briefly in the caption
Collaborative Goal Setting
- Define strategic planning objectives based on the evaluation findings from your analysis
- Ideally, involve the community of your living labs into this process
- Link back to your original targets from section one and the Development Goals
- 150 words text contribution
Spatial Strategy and Transect
- translate your strategic goals into a vision
- develop a spatial translation of your vision
- exemplify your vision in the form of a transect with concrete interventions
- add map(s) and visualizations
- Your case spatial translaton vision.jpg
add caption here
- Your case transect.jpg
add caption here
- Your case transect detail1.jpg
add caption here
- Your case transect detail2.jpg
add caption here
From Theory of Change to Implementation
- For implementing your vision: Which partnerships are needed? Which governance model is required?
- Who needs to act and how? Draw and explain a change/process model/timeline
- Which resources are needed? On which assets can you build?
- add 150 words text and visuals
References
- give a full list of the references you have used for your case
Process Reflection
- Reflect in your intercultural and interdisciplinary team on the outcomes of your study
- Which limitations were you facing?
- What have you learnt from each other?
- What did you learn in the Living Labs?
- What would you do differently next time?
- You can also use diagrams/visuals
- 250 words text